
Of the patients, 98.07% were Rh positive. Results: In the 2,586 COVID-19-infected patients, the frequencies of A, B, O, and AB were 29.93%, 41.80%, 21.19%, and 7.98%, respectively. Data was analyzed using chi-square test, odds ratio, and Mann–Whitney test to determine the association of blood groups. Patients were enrolled from Apto October 4, 2020. A total of 2,586 real-time PCR (RT-PCR)-confirmed coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients were recruited. We investigated the association of ABO and Rh blood groups with susceptibility to coronavirus disease 2019 infection, severity of disease, recovery period, and mortality of patients. Methods: This is a single-center, retrospective study conducted at Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, Delhi. Studies have shown association of blood groups A and O with higher and lower odds for coronavirus disease 2019 positivity, respectively. 2Department of Blood Transfusion Medicine, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, Indiaīackground: ABO and Rh blood group systems are associated with many diseases including cancerous, infectious, non-infectious, bacterial and viral diseases.1Department of Research, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, India.Pregnant women typically receive RhoGAM twice during their pregnancy: once at approximately 28 weeks and once within 72 hours of delivery, if in fact, the newborn baby is Rh positive.Rashmi Rana 1*†, Vivek Ranjan 2† and Naveen Kumar 1† HDN can cause serious illnesses, brain damage or even death in a fetus or newborn. If she does not receive the injection, her body will develop antibodies that could attack the positive red blood cells of babies in subsequent pregnancies, which will cause HDN. When a woman receives RhoGAM, it protects her immune system from the exposure to the current baby’s Rh-positive blood.
.jpg)
If a woman is Rh negative, she will most likely receive a RhoGAM injection. Since more people are Rh positive than Rh negative, it is likely that an Rh-negative mother could be carrying a baby who is Rh positive, creating the risk for hemolytic disease of a newborn (HDN) in future pregnancies, essentially destroying that baby’s red blood cells. Once a woman finds out she is pregnant, her doctor will test her blood to determine her Rh factor. If a pregnant woman who is Rh negative does not receive RhoGAM, and is carrying an Rh-positive baby, she risks the health of future pregnancies because she has been exposed to the positive blood from her current unborn baby. It is used to prevent an immune response in mothers who are Rh negative. RhoGAM, or Rho(d) Immune Globulin Human, is a sterilized solution made from human blood. This led to the development and FDA-approval of RhoGAM® in 1968. When Landsteiner and Weiner discovered the Rh protein, they were researching solutions for the cause of a medical mystery that killed dozens of babies each day. Only people with at least one Rh-negative factors will have a negative blood type, which is why the occurrence of Rh-negative blood is less common than Rh-positive blood. For example, if someone’s Rh factors are both positive, it is not possible for his or her child to have a negative blood type. The only way for someone to have a negative blood type is for both parents to have at least one negative factor. Each person has two Rh factors in their genetics, one from each parent. Just as we inherit our blood type “letter” from our parents, we inherit the Rh factor from them as well. In the United States, approximately 85% of the population has an Rh-positive blood type, leaving only 15% with Rh negative. However, when it comes to the Rh blood types, many of us do not fully understand what it means to be positive or negative.
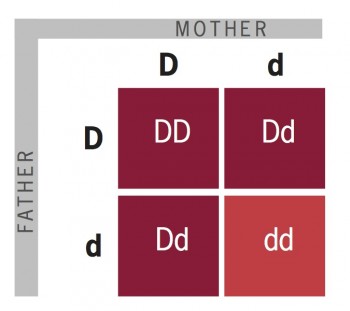
To put it simply, Landsteiner and Weiner discovered that blood types can be either Rh positive or Rh negative, doubling the commonly known blood types from four (A, B, AB, and O), to the eight we know today. When it comes to blood transfusion, anyone who is Rh positive can receive blood from someone who is Rh negative, but those with negative blood types cannot receive from anyone with a positive blood type. This protein is also often called the D antigen. The rhesus protein is named for the rhesus monkey, which also carries the gene, and is a protein that lives on the surface of the red blood cells.

In 1937, Karl Landsteiner and Alexander Weiner discovered a new blood type: the rhesus blood type, or Rh factor. Knowing your blood type can play a significant role in your life and health. Although we have become accustomed to adding a positive or negative description to our blood type, the Rh factor plays a larger role than many of us realize.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
